Macedonians (ethnic group)
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1st row: Gjorgji Pulevski[1], Krste Misirkov[1], Hristijan Todorovski Karpoš, Metodija Andonov-Čento, Lazar Koliševski |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,000,000 - 2,500,000[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regions with significant populations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
predominantly † Macedonian Orthodox |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related ethnic groups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
South Slavs |
The Macedonians (Macedonian: Македонци; transliterated: Makedonci) – also referred to as Macedonian Slavs[34] – are a South Slavic people who are primarily associated with the Republic of Macedonia. They speak the Macedonian language, a South Slavic language. About two thirds of all ethnic Macedonians live in the Republic of Macedonia and there are also communities in a number of other countries. It is generally believed that the ethnic Macedonian identity emerged in the late 19th century.[35][36] [37][38][39]
Contents |
Origins
The ancestry of present-day Macedonians is mixed: their linguistic and cultural origins stem largely from the 6th century "migrations"[40] of various Slavic tribes to southeast Europe, yet genetically they are an amalgamation of the various peoples and civilizations that have inhabited the area throughout history. Some early 20th century researchers as William Z. Ripley, Coon[41] and Bertil Lundman[42] described the Slavic speakers in Macedonia as Bulgarians, and often placed both populations in a common racial subgroup. Other authors, like H. N. Brailsford, described Slavic speakers from Macedonia as related to both Serbs and Bulgarians, but without clear defined ethnic consciousness. Brailsford considered a part of the people of North West Macedonia as Serbs and the people of the region of Ohrid as Bulgarians.[43]
The Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts accepts that as a whole the modern Macedonian genotype developed as a result of the absorption by the advancing Slavs of the local peoples living in the region of Macedonia prior to their coming. This position is backed by the findings of most ethnographers such as Vasil Kanchov,[44] Gustav Weigand,[45] and the anthropologist Carleton S. Coon, which state that the Slavs in 6th century actively assimilated other tribal peoples by absorbing part of the indigenous populations of the area, including Greeks, Thracians and Illyrians.[46][47] By absorbing parts of the peoples living there the Slavs also absorbed their culture, and in that amalgamation a people was gradually formed with predominantly Slavic ethnic elements, speaking a Slavonic language and with a Slavic-Byzantine culture. Furthermore, the genetic studies support the theories that Macedonians genetic heritage is derived from a mixture of ancient Balkan peoples[48] as well as the relatively newly arrived Slavs with deep European roots.
Population genetics studies using HLA loci have been used in light of unanswered questions regarding Macedonians' origins and relationship with other populations.[49] Macedonians are most closely related to other Balkanians as Croats, Serbs, Greeks, Bulgarians and Romanians.[50][51][52][53] It is also corroborated that there is some non-European inflow in modern Macedonians.[54]
Population
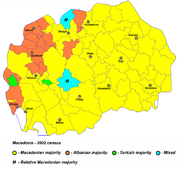
The vast majority of ethnic Macedonians live along the valley of the river Vardar, the central region of the Republic of Macedonia. They form about 64.18% of the population of the Republic of Macedonia (1,297,981 people according to the 2002 census). Smaller numbers live in eastern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern Greece, and southern Serbia, mostly abutting the border areas of the Republic of Macedonia. A large number of Macedonians have immigrated overseas to Australia, United States, Canada and in many European countries: Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, and Austria, among others.
Macedonians in the Balkans
| Part of a series on |
| Macedonians |
|---|
 |
| By region or country |
| Macedonia (region) |
| Republic of Macedonia Greece · Albania · Bulgaria |
| Diaspora |
| Balkans Serbia · Slovenia · Croatia |
| Elsewhere in Europe Czech Republic Denmark · France Germany · Poland Romania · Sweden Switzerland · United Kingdom |
| Americas Argentina · Brazil Canada · United States |
| Oceania Australia |
| Subgroups/Related groups |
| Macedonian Muslims Torlaks/Pomaks · Gorani Mijaks · Šopi |
| Culture |
| Art · Cinema · Cuisine Language · Literature Music · Symbols |
| Religion |
| Macedonian Orthodoxy Islam · Roman Catholicism Protestantism · Judaism |
| History |
| Macedonian awakening Ilinden Uprising National Liberation War ASNOM National Liberation Front Exodus from Greece Socialist Republic of Macedonia Republic of Macedonia |
| Other topics |
| List of Macedonians Macedonian nationalism Holidays
|
Greece

The existence of an ethnic Macedonian minority in Greece is rejected by the Greek government. Such claims are directed at the Slavic-speaking community of northern Greece, which dominantly self-identifies as Slavophone Greeks.[55] and defines its language as "Slavic" or Dopia (a Greek word for 'local'). This community numbered 41,017 people according to the latest Greek census to include a question on mother tongue held in 1951, and local authorities in Greece continue to acknowledge its existence. Other estimates of the number of Slavophones in Greece range from 180,000 to 300,000.[56][57][58][59][60][61][62][63][64]
The size of the community identifying as ethnic "Macedonians" today is estimated by the Greek Helsinki Monitor, at around 10,000-30,000[65] any others resenting having their Hellenism questioned. GHM is basing this figure on the electoral performance of the ethnic Macedonian political party the region of Greek Macedonia: the Rainbow, which received 7,300 votes in 1994 elections and 5,000 in 1999 elections. In 2007, it did not stand for elections. The overwhelming majority of Greece's Slavic-speaking community is composed of people with Greek consciousness, which are pejoratively referred to with the term Grkomani by people in the Republic of Macedonia and trans-national ethnic Macedonian communities.[66] In 1993, at the height of the name controversy and just before joining the UN, the government in Skopje claimed that there were between 230,000 and 270,000 Macedonians living in northern Greece.
Serbia

<7000 1000-2000 500-1000 100-500
Serbia recognizes the Macedonian minority on its territory as a distinct ethnic group and counts them in its annual census. 25,847 people declared themselves Macedonians in the 2002 census. There are many Macedonian concentrations in the Vojvodina region. Macedonians made up a significant minority in the municipalities of Plandiste, Jabuka, Glogonj, Dužine and Kacarevo.In these areas they are over 25% of the population. They are mainly economic migrants from the Socialist Republic of Macedonia who left in the 1960s and 1970s due to the worsening economic situation back home. Currently there is no specific program to educate students in Macedonian. Yet there are attempts to introduce Macedonian language classes into areas where there is a significant minority.
Albania
Albania recognizes ethnic Macedonians as an ethnic minority and delivers primary education in the Macedonian language in the border regions where most ethnic Macedonians live. In the 1989 census, 4,697 people declared themselves ethnic Macedonians.[67] Ethnic Macedonian organizations allege that the government undercounts their number and that they are politically under-represented — there are no ethnic Macedonians in the Albanian parliament. Some say that there has been disagreement among the Slav-speaking Albanian citizens about their being members of a Macedonian nation as a significant percentage of their number are Torbeš and self-identify as Albanians. External estimates on the population of ethnic Macedonians in Albania include 10,000,[68] whereas ethnic Macedonian sources have claimed that there are 120,000 - 350,000 ethnic Macedonians in Albania.
Bulgaria
In the 2001 census in Bulgaria, 5,071 people declared themselves ethnic Macedonians (see the official data in Bulgarian here). Krassimir Kanev, chairman of the non-governmental organization (NGO) Bulgarian Helsinki Committee, claimed 15,000 - 25,000 in 1998 (see here). In the same report Macedonian nationalists (Popov et al., 1989) claimed that 200,000 ethnic Macedonians live in Bulgaria. However, Bulgarian Helsinki Committee stated that the vast majority of the Slavic population in Pirin Macedonia has a Bulgarian national self-consciousness and a regional Macedonian identity similar to the Macedonian regional identity in Greek Macedonia. Finally, according to personal evaluation of a leading local ethnic Macedonian political activist, Stoyko Stoykov, the present number of Bulgarian citizens with ethnic Macedonian self-consciousness is between 5,000 and 10,000.[69] Macedonian groups in the country have reported official harassment. The Bulgarian Constitutional Court banned UMO Ilinden-Pirin, a small Macedonian political party, in 2000 as separatist and Bulgarian local authorities banned its political rallies. UMO Ilinden-Pirin claims that the minority has experienced a period of intensive assimilation and repression.
Population estimates
The Macedonian Diaspora

Republic of Macedonia Recognised minority 50,000+ 20,000+ 4,000+ 800+
Significant Macedonian communities can also be found in the traditional immigrant-receiving nations, as well as in Western European countries. It should be noted that census data in many European countries (such as Italy and Germany) does not take into account the ethnicity of émigrés from the Republic of Macedonia:
- Argentina: Many Macedonians of Argentina are the descendants of the "pečalbari" (seasonal workers) who came to Argentina in the early 20th century. Many decided to stay in Argentina setting up Macedonian colonies in the Pampas and other regions. Most Macedonians can be found in Buenos Aires, the Pampas and Córdoba. An estimated 30,000 Macedonians can be found in Argentina.[5]
- Australia: The official number of Macedonians in Australia by birthplace or birthplace of parents is 83,893 (2001). The main Macedonian communities are found in Melbourne, Geelong, Sydney, Wollongong, Newcastle, Canberra and Perth. (The 2006 Australian Census included a question of 'ancestry' which, according to Members of the Australian-Macedonian Community, this will result in a 'significant' increase of 'ethnic Macedonians' in Australia. However, the 2006 census recorded 83,983 people of Macedonian (ethnic) ancestry.) See also Macedonian Australians;
- Canada: The Canadian census in 2001 records 37,705 individuals claimed wholly or partly Macedonian heritage in Canada,[70] although community spokesmen have claimed that there are actually 100,000-150,000 Macedonians in Canada[71] (see also Macedonian Canadians);
- USA: A significant Macedonian community can be found in the United States of America. The official number of Macedonians in the USA is 49,455 (2004). The Macedonian community is located mainly in Michigan, New York, Ohio, Indiana and New Jersey[72] (See also Macedonian Americans);
- Germany: There are an estimated 61,000 citizens of the Republic of Macedonia in Germany (mostly in the Ruhrgebiet) (2001) (See also Ethnic Macedonians in Germany);
- Italy: There are 74, 162 citizens of the Republic of Macedonia in Italy (Foreign Citizens in Italy).
- Switzerland: In 2006 the Swiss Government recorded 60,362 Macedonian Citizens living in Switzerland. (See also Macedonians in Switzerland)[73]
- Romania: Ethnic Macedonians are an officially recognised minority group in Romania. They have a special reserved seat in the nations parliament. In 2002, they numbered 731. (see also Macedonians in Romania)
- Slovenia: Ethnic Macedonians began relocating to Slovenia in the 1950s when the two regions formed a part of a single country, Yugoslavia (see also Macedonians in Slovenia).
Other significant ethnic Macedonian communities can also be found in the other Western European countries such as Austria, France, Switzerland, Netherlands, United Kingdom, etc. Also in Uruguay, with a significant population in Montevideo.
Culture
The culture of the Macedonian people is characterized with both traditionalist and modernist attributes. It is strongly bound with their native land and the surrounding in which they live. The rich cultural heritage of the Macedonians is accented in the folklore, the picturesque traditional folk costumes, decorations and ornaments in city and village homes, the architecture, the monasteries and churches, iconostasis, wood-carving and so on. The culture of Macedonians can roughly be explained as a Balkanic, closely related to that of Serbs and Bulgarians.
Architecture

The typical Macedonian village house is presented as a construction with two floors, with a hard facade composed of large stones and a wide balcony on the second floor. In villages with predominantly agricultural economy, the first floor was often used as a storage for the harvest, while in some villages the first floor was used as a cattle-pen.
The stereotype for a traditional Macedonian city house is a two-floor building with white façade, with a forward extended second floor, and black wooden elements around the windows and on the edges.
Cinema and theater
The history of film making in the Republic of Macedonia dates back over 110 years. The first film to be produced on the territory of the present-day the country was made in 1895 by Janaki and Milton Manaki in Bitola. From then, continuing the present, Macedonian film makers, in Macedonia and from around the world, have been producing many films.
From 1993-1994 1,596 performances were held in the newly formed republic, and more than 330,000 people attended. The Macedonian National Theater (Drama, Opera and Ballet companies), the Drama Theater, the Theater of the Nationalities (Albanian and Turkish Drama companies) and the other theater companies comprise about 870 professional actors, singers, ballet dancers, directors, playwrights, set and costume designers, etc. There is also a professional theatre for children and three amateur theaters. For the last thirty years a traditional festival of Macedonian professional theaters has been taking place in Prilep in honor of Vojdan Černodrinski, the founder of the modern Macedonian theater. Each year a festival of amateur and experimental Macedonian theater companies is held in Kočani.
Music and art
Macedonian's music has an exceptionally rich musical heritage. Their music has many things in common with the music of neighboring Balkan countries, but maintains its own distinctive sound.
The founders of modern Macedonian painting included Lazar Licenovski, Nikola Martinoski, Dimitar Pandilov, and Vangel Kodzoman. They were succeeded by an exceptionally talented and fruitful generation, consisting of Borka Lazeski, Dimitar Kondovski, Petar Mazev who are now deceased, and Rodoljub Anastasov and many others who are still active. Others include: Vasko Taskovski and Vangel Naumovski. In addition to Dimo Todorovski, who is considered to be the founder of modern Macedonian sculpture, the works of Petar Hadzi Boskov, Boro Mitrikeski, Novak Dimitrovski and Tome Serafimovski are also outstanding.
Economy
In the past, the Macedonian population was predominantly involved with agriculture, with a very small portion of the people who were engaged in trade (mainly in the cities). But after the creation of the People’s Republic of Macedonia which started a social transformation based on Socialist principles, a middle and hard industry was being created.
Language
The Macedonian language (македонски јазик) is a member of the Eastern group of South Slavic languages. Standard Macedonian was implemented as the official language of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia after being codified in the 1940s, and has accumulated a thriving literary tradition.
The closest relative of Macedonian is Bulgarian,[74] followed by Serbo-Croatian. All the South Slavic languages, including Macedonian, form a dialect continuum, in which Macedonian is situated between Bulgarian and Serbian. The Torlakian dialect group is intermediate between Bulgarian, Macedonian and Serbian, comprising some of the northernmost dialects of Macedonian as well as varieties spoken in southern Serbia.
The orthography of Macedonian includes an alphabet, which is an adaptation of the Cyrillic alphabet, as well as language-specific conventions of spelling and punctuation.
Religion
Most Macedonians are members of the Macedonian Orthodox Church. The official name of the church is Macedonian Orthodox Church – Ohrid Archbishopric and is the body of Christians who are united under the Archbishop of Ohrid and Macedonia, exercising jurisdiction over Macedonian Orthodox Christians in the Republic of Macedonia and in exarchates in the Macedonian diaspora.
The church gained autonomy from the Serbian Orthodox Church in 1959 and declared the restoration of the historic Archbishopric of Ohrid. On July 19, 1967, the Macedonian Orthodox Church declared autocephaly from the Serbian church, a move which is not recognised by any of the churches of the Eastern Orthodox Communion, and since then, the Macedonian Orthodox Church is not in communion with any Orthodox Church.
Between the 15th and the 20th century, during the Ottoman rule, a large number of Orthodox Macedonian Slavs converted to Islam. Today in the Republic of Macedonia they are regarded as Macedonian Muslims. A small number of Macedonians belong to the Protestant and the Roman Catholic churches.
.
Names
Main article: Macedonian Names
Cuisine

Macedonian cuisine is a representative of the cuisine of the Balkans—reflecting Mediterranean (Greek and Turkish) and Middle Eastern influences, and to a lesser extent Italian, German and Eastern European (especially Hungarian) ones. The relatively warm climate in Macedonia provides excellent growth conditions for a variety of vegetables, herbs and fruits. Thus, Macedonian cuisine is particularly diverse.
Famous for its rich Shopska salad, an appetizer and side dish which accompanies almost every meal, Macedonian cuisine is also noted for the diversity and quality of its dairy products, wines, and local alcoholic beverages, such as rakija. Tavče Gravče and mastika are considered the national dish and drink of the Republic of Macedonia, respectively.
Identities
- See also: Macedonian Question and National awakening of the ethnic Macedonians
Macedonians are people with a unique identity derived from an influence of different cultures. The large majority identify themselves as Orthodox Christians, who speak a Slavic language, and share similarities in culture with their Balkan neighbours. The concept of a distinct "Macedonian" ethnicity is seen as a relatively new arrival to the milieu of peoples that is the Balkans. Modern ethnographers consider that, until the early 20th century, the Slavic speaking majority in the Region of Macedonia were by in large Bulgarian.[75][76][77] However, in the late 19th and early 20th century some intellectuals began to propagated that the Slavic-speakers of Macedonia compose a separate ethnicity, which is different from their neighbours. This was the time of the first expressions of ethnic nationalism which occurred in Belgrade, Sofia, Istanbul, Thessaloniki and St. Petersburg. The activities of these people was registered by Petko Slaveykov[78] and Stojan Novaković[79]
The first prominent author that propagated the separate ethnicity of the Macedonians was Georgi Pulevski, who in 1875 published Dictionary of Three languages: Macedonian, Albanian, Turkish, in which he wrote:
"What do we call a nation"? "People who are of the same origin and who speak the same words and who live and make friends of each other, who have the same customs and songs and entertainment are what we call a nation, and the place where that people lives is called the people's country. Thus the Macedonians also are a nation and the place which is theirs is called Macedonia."
On the other hand Theodosius of Skopje, a priest who have hold a high ranking positions within the Bulgarian Exarchate was chosen as a bishop of the episcopacy of Skopje in 1885. As a bishop of Skopje, Theodosius renounced de facto the Bulgarian Exarchate and attempted to restore the Archbishopric of Ohrid and to separate the episcopacies in Macedonia from the Exarchate.[80] During this time period Metropolitan Bishop Theodosius of Skopje made several pleas to the Bulgarian church to allow a separate Macedonian church, he viewed this as the only way to end the turmoil in the Balkans.
In 1903 Krste Petkov Misirkov published his book On Macedonian Matters in which he laid down the principles of the modern Macedonian nationhood and language. This book is considered by ethnic Macedonians as a milestone of the ethnic Macedonian identity and the apogee of the process of Macedonian awakening. In his article "Macedonian Nationalism" he wrote:
I hope it will not be held against me that I, as a Macedonian, place the interests of my country before all... I am a Macedonian, I have a Macedonian's consciousness, and so I have my own Macedonian view of the past, present, and future of my country and of all the South Slavs; and so I should like them to consult us, the Macedonians, about all the questions concerning us and our neighbours, and not have everything end merely with agreements between Bulgaria and Serbia about us – but without us.
The next great figure of the Macedonian awakening was Dimitrija Čupovski, one of the founders of the Macedonian Literary Society, established in Saint Petersburg in 1902. In the period 1913-1918, Čupovski published the newspaper Македонскi Голосъ (Macedonian Voice) in which he and fellow members of the Petersburg Macedonian Colony propagated the existence of a Macedonian people separate from the Greeks, Bulgarians and Serbs, and sought to popularize the idea for an independent Macedonian state.
After the Balkan Wars, following division of the region of Macedonia amongst the Kingdom of Greece, the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the Kingdom of Serbia, and after World War I, the idea of belonging to a separate Macedonian nation was further spread among the Slavic-speaking population. The suffering during the wars, the endless struggle of the Balkan monarchies for dominance over the population increased the Macedonians' sentiment that the institutionalization of an independent Macedonian nation would put an end to their suffering. On the question of whether they were Serbs or Bulgarians, the people more often started answering: "Neither Bulgar, nor Serb... I am Macedonian only, and I'm sick of war."[81][82]
The first political organization that promoted the existence of a separate ethnic Macedonian nation was Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (United),[83] composed of former left-wing Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) members and founded in 1925. This idea was internationalized and backed by the Comintern which issued in 1934 a declaration supporting the development of the entity.[84] This action was attacked by the IMRO, but was supported by the Balkan communists. The Balkan communist parties supported the national consolidation of the ethnic Macedonian people and created Macedonian sections within the parties, headed by prominent IMRO (United) members. The sense of belonging to a separate Macedonian nation gained credence during World War II when ethnic Macedonian partisan detachments were formed, and especially after World War II when ethnic Macedonian institutions were created in the three parts of the region of Macedonia,[85] including the establishment of the People's Republic of Macedonia within the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRJ).
History
The history of the ethnic Macedonians is closely associated with the historical and geographical region of Macedonia, and is manifested with their constant struggle for an independent state. After many decades of insurrections and living through several wars, the Macedonians in World War II managed to create their own country.
Symbols
- See also: Flags of the Republic of Macedonia, Symbols of the Republic of Macedonia
|
||
|
- Sun: The official flag of the Republic of Macedonia, adopted in 1995, is a yellow sun with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field.
- Coat of Arms: After independence in 1992, the Republic of Macedonia retained the coat of arms adopted in 1946 by the People's Assembly of the People's Republic of Macedonia on its second extraordinary session held on July 27, 1946, later on altered by article 8 of the Constitution of the Socialist Federal Republic of Macedonia. The coat-of-arms is composed by a double bent garland of ears of wheat, tobacco and poppy, tied by a ribbon with the embroidery of a traditional folk costume. In the center of such a circular room there are mountains, rivers, lakes and the sun. All this is said to represent "the richness of our country, our struggle, and our freedom".
Unofficial symbols
- Lion: The lion first appears in the Fojnica Armory from 1340,[86] where the coat of arms of Macedonia is included among with those of other countries. On the coat of arms is a crown, inside a yellow crowned lion is depicted standing rampant, on a red background. On the bottom enclosed in a red and yellow border is written "Macedonia". The use of the lion to represent Macedonia was continued in foreign heraldic collections throughout the 15th to 18th centuries.[87][88] Modern versions of the historical lion has also been added to the emblem of several political parties, organizations and sports clubs.
- Vergina Sun: (official flag, 1992–1995) The Vergina Sun is used by various associations and cultural groups in the Macedonian diaspora. The Vergina Sun is believed to have been associated with ancient Greek kings such as Alexander the Great and Philip II, although it was used as an ornamental design long before the Macedonian period. The symbol was discovered in the present-day Greek region of Macedonia and Greeks regard it as a misappropriation of a Hellenic symbol, unrelated to Slavic cultures, and a direct claim on the legacy of Philip II. Greece had the Vergina Sun copyrighted under WIPO as a State Emblem of Greece in the 1990s.[89] The Vergina sun on a red field was the first flag of the independent Republic of Macedonia, until it was removed from the state flag under an agreement reached between the Republic of Macedonia and Greece in September 1995.[90] The Vergina sun is still used[91] unofficially as a national symbol by some groups in the country and Macedonian diaspora.
Macedonians through history
 Georgi Pulevski[1], one of the first authors that separated the Macedonian nation from the others. |
 Theodosius of Skopje[1], a religious figure, the first who attempted to make a Macedonian Uniat Church. |
 Goce Delčev, IMRO revolutionary, national hero in both Bulgaria and the Republic of Macedonia. Considered an ethnic Macedonian in the latter. |
 Krste Petkov Misirkov[1]. |
 Dimitrija Čupovski, Macedonian textbook writer and lexicographer |
 Risto Krle, playwright. |
Mirče Acev, Macedonian and Yugoslav partisan. |
Čede Filipovski Dame, Macedonian partisan (On the picture: Memorial to Dame in Gostivar, Macedonia). |
 Kočo Racin, poet and revolutionary (On the picture: Memorial to Racin in Samobor, Croatia). |
 Aleksandar Sarievski, folk singer. |
 Milčo Mančevski, film director and screen writer. |
 Ed Jovanovski, National Hockey League player. |
|
Pasko Kuzman, prominent archaeologist. |
 Blagoj Nacoski, tenor opera singer. |
 Darko Dimitrov, composer. |
 Darko Pančev, retired Macedonian and Yugoslav footballer |
 Karolina Gočeva, singer. |
 Kiril Lazarov, handball player. |
Goran Pandev, football striker. |
 Toše Proeski, singer and humanitarian. |
 Kaliopi, singer and songwriter. |
 Katarina Ivanovska, international model. |
Elena Risteska, singer and songwriter. |
See also
- Demographic history of Macedonia
- List of Macedonians
- Demographics of the Republic of Macedonia
- Macedonian language
- Ethnogenesis
- South Slavs
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 People that are considered to be Bulgarians in Bulgaria and Macedonians in the Republic of Macedonia.
- ↑ Nasevski, Boško; Angelova, Dora. Gerovska, Dragica (1995). Македонски Иселенички Алманах '95. Skopje: Матица на Иселениците на Македонија. pp. 52 & 53.
- ↑ 2002 census.
- ↑ 2006 Census.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Population Estimate from the MFA.
- ↑ Foreign Citizens in Italy, 2007.
- ↑ 2006 figures.
- ↑ 2005 Figures.
- ↑ 2007 Community Survey.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Nasevski, Boško; Angelova, Dora. Gerovska, Dragica (1995). Македонски Иселенички Алманах '95. Skopje: Матица на Иселениците на Македонија. pp. 52 & 53.
- ↑ Mac. Information Agency
- ↑ 2006 census.
- ↑ 2001 census.
- ↑ 2002 census.
- ↑ 2001 census - Tabelle 13: Ausländer nach Staatsangehörigkeit (ausgewählte Staaten), Altersgruppen und Geschlecht — p. 74.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 1996 Estimate.
- ↑ 1.2001 Bulgarian census data.
- ↑ Center for Documentation and Information on Minorities in Europe, Southeast Europe (CEDIME-SE) - "Macedonians of Bulgaria".
- ↑ http://www.fes.hr/E-books/pdf/Local%20Self%20Government/09.pdf Artan Hoxha and Alma Gurraj "LOCAL SELF-GOVERNMENT AND DECENTRALIZATION: CASE OF ALBANIA. HISTORY, REFORMES AND CHALLENGES" "...According to latest Albanian census conducted in April 1989, 98% of Albanian population are Albanian ethnic. The remaining 2% (or 64816 people) belong to ethnic minorities: the vast majority is composed by ethnic Greeks (58758 ); ethnic Macedonians (4697)...",[1], Joshua Project.
- ↑ OECD Statistics.
- ↑ 2002 census.
- ↑ 2002 census.
- ↑ 2006 census.
- ↑ "Belgium population statistics". www.dofi.fgov.be. http://www.dofi.fgov.be/fr/statistieken/statistiques_etrangers/Stat_ETRANGERS.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- ↑ 2008 census.
- ↑ 2008 figures.
- ↑ 2003 census,Population Estimate from the MFA.
- ↑ 2005 census.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Makedonci vo Svetot.
- ↑ Polands Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947, p. 260.
- ↑ "Data on immigrants in Greece, from Census 2001". Migrants in Greece. http://migrantsingreece.org/transpartner/Tables.pdf. Retrieved 2009-01-12.
- ↑ "Greece – Report about Compliance with the Principles of the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (along guidelines for state reports according to Article 25.1 of the Convention)". Greek Helsinki Monitor (GHM) & Minority Rights Group – Greece (MRG-G). 1999-09-18. http://dev.eurac.edu:8085/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1044526702223. Retrieved 2009-01-12.
- ↑ Montenegrin 2003 census -.
- ↑ "Macedonian Slavs" can be translated into Macedonian as Македонски Словени (Makedonski Sloveni). "Slavs" is the primary qualifier used by scholars in order to disambiguate the ethnic Macedonians from all other Macedonians in the region (see Google scholar for instance). Krste Misirkov himself used the same qualifier numerous times in one of the first ethnic Macedonian patriotic texts "On Macedonian Matters" (most of the text in English here). The Slav Macedonians in Greece were happy to be acknowledged as "Slavomacedonians". A native of Greek Macedonia, a pioneer of Slav Macedonian schools in the region and a local historian, Pavlos Koufis, wrote in Laografika Florinas kai Kastorias (Folklore of Florina and Kastoria), Athens 1996, that (translation by User:Politis),
However, the current use of "Slavomacedonian" in reference to both the ethnic group and the language, although acceptable in the past, can be considered pejorative and offensive by some ethnic Macedonians living in Greece. The Greek Helsinki Monitor reports:"[During its Panhellenic Meeting in September 1942, the KKE mentioned that it recognises the equality of the ethnic minorities in Greece] the KKE recognised that the Slavophone population was ethnic minority of Slavomacedonians]. This was a term, which the inhabitants of the region accepted with relief. [Because] Slavomacedonians = Slavs+Macedonians. The first section of the term determined their origin and classified them in the great family of the Slav peoples."
: "... the term Slavomacedonian was introduced and was accepted by the community itself, which at the time had a much more widespread non-Greek Macedonian ethnic consciousness. Unfortunately, according to members of the community, this term was later used by the Greek authorities in a pejorative, discriminatory way; hence the reluctance if not hostility of modern-day Macedonians of Greece (i.e. people with a Macedonian national identity) to accept it." - ↑ Sperling, James; Kay, Sean; Papacosma, S. Victor (2003). Limiting institutions?: the challenge of Eurasian security governance. Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press. pp. 57. ISBN 978-0-7190-6605-4. "Macedonian nationalism Is a new phenomenon. In the early twentieth century, there was no separate Slavic Macedonian identity"
- ↑ Titchener, Frances B.; Moorton, Richard F. (1999). The eye expanded: life and the arts in Greco-Roman antiquity. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 259. ISBN 978-0-520-21029-5. "On the other hand, the Macedonians are a newly emergent people in search of a past to help legitimize their precarious present as they attempt to establish their singular identity in a Slavic world dominated historically by Serbs and Bulgarians. ... The twentieth-century development of a Macedonian ethnicity, and its recent evolution into independent statehood following the collapse of the Yugoslav state in 1991, has followed a rocky road. In order to survive the vicissitudes of Balkan history and politics, the Macedonians, who have had no history, need one."
- ↑ Kaufman, Stuart J. (2001). Modern hatreds: the symbolic politics of ethnic war. New York: Cornell University Press. pp. 193. ISBN 0-8014-8736-6. "The key fact about Macedonian nationalism is that it is new: in the early twentieth century, Macedonian villagers defined their identity religiously—they were either “Bulgarian,” “Serbian,” or “Greek” depending on the affiliation of the village priest. ... According to the new Macedonian mythology, modern Macedonians are the direct descendants of Alexander the Great’s subjects. They trace their cultural identity to the ninth-century Saints Cyril and Methodius, who converted the Slavs to Christianity and invented the first Slavic alphabet, and whose disciples maintained a centre of Christian learning in western Macedonia. A more modern national hero is Gotse Delchev, leader of the turn-of-the-century Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), which was actually a largely pro-Bulgarian organization but is claimed as the founding Macedonian national movement."
- ↑ Rae, Heather (2002). State identities and the homogenisation of peoples. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 278. ISBN 0-521-79708-X. "Despite the recent development of Macedonian identity, as Loring Danforth notes, it is no more or less artificial than any other identity. It merely has a more recent ethnogenesis - one that can therefore more easily be traced through the recent historical record."
- ↑ Zielonka, Jan; Pravda, Alex (2001). Democratic consolidation in Eastern Europe. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 422. ISBN 978-0-19-924409-6. "Unlike the Slovene and Croatian identities, which existed independently for a long period before the emergence of SFRY Macedonian identity and language were themselves a product federal Yugoslavia, and took shape only after 1944. Again unlike Slovenia and Croatia, the very existence of a separate Macedonian identity was questioned—albeit to a different degree—by both the governments and the public of all the neighboring nations (Greece being the most intransigent)"
- ↑ NB: The extent of the migrations reported by 6th century sources is under considerable debate today. Whilst no one discounts Slavic raids into the Balkans, the number of actual immigrants, and the state of the 'native' population is not known for sure. As somewhat of a contrary, but not mutually exclusive, to 'traditionalist' migration scenarios, newer explanations see the Slavonization of the Balkans as part of a widespread cultural-economic re-orientation of the Balkan provincials away from a Greco-Roman-Meditteranean civilizaiton to a central European Slavic-Avar one. See 'The Making of the Slavs", Florin Curta & "Beconing Slav, Becoming Croat", Danijel Dzino. This is analogous to current debates amongst English scholars regarding the so-called Anglo-Saxon migrations in post-Roman Britain. Eg see generally "Barbarian Migrations and the Roman West", by Guy Halsall
- ↑ in his book The Races Of Europe.
- ↑ Lundman, Bertil J. - The Races and Peoples of Europe (New York: IAAEE. 1977)[2].
- ↑ MACEDONIA: Its races and their future. H. N. Brailsford, London, 1906. p. 101.
- ↑ Пътуване по долините на Струма, Места и Брегалница. Битолско, Преспа и Охридско. Васил Кънчов (Избрани произведения. Том I. Издателство "Наука и изкуство", София 1970) [3].
- ↑ (ETHNOGRAPHIE VON MAKEDONIEN, Geschichtlich-nationaler, spraechlich-statistischer Teil von Prof. Dr. Gustav Weigand, Leipzig, Friedrich Brandstetter, 1924, Превод Елена Пипилева)[4].
- ↑ "Macedonia :: History. – Encyclopaedia Britannica". http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-4411/Macedonia. Retrieved 2007-08-27.
- ↑ Coon, Carleton Stevens (1975). The Races of Europe. Greenwood Press Reprint. ISBN 0-8371-6328-5., Chapter XII, section 15[5].
- ↑ Rebala K et al. (2007), Y-STR variation among Slavs: evidence for the Slavic homeland in the middle Dnieper basin, Journal of Human Genetics, 52:406-14.
- ↑ Petlichkovski A, Efinska-Mladenovska O, Trajkov D, Arsov T, Strezova A, Spiroski M (2004). "High-resolution typing of HLA-DRB1 locus in the Macedonian population". Tissue Antigens 64 (4): 486–91. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2004.00273.x. PMID 15361127.
- ↑ Ivanova M, Rozemuller E, Tyufekchiev N, Michailova A, Tilanus M, Naumova E (2002). "HLA polymorphism in Bulgarians defined by high-resolution typing methods in comparison with other populations". Tissue Antigens 60 (6): 496–504. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0039.2002.600605.x. PMID 12542743.
- ↑ Bulgarian Bone Marrow Donors Registry—past and future directions — Asen Zlatev, Milena Ivanova, Snejina Michailova, Anastasia Mihaylova and Elissaveta Naumova, Central Laboratory of Clinical Immunology, University Hospital "Alexandrovska", Sofia, Bulgaria, Published online: 2 June 2007 [6].
- ↑ "European Journal of Human Genetics - Y chromosomal heritage of Croatian population and its island isolates.". http://www.nature.com/ejhg/journal/v11/n7/full/5200992a.html.
- ↑ Semino, Ornella; Passarino, G; Oefner, PJ; Lin, AA; Arbuzova, S; Beckman, LE; De Benedictis, G; Francalacci, P et al. (2000). "The Genetic Legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in Extant Europeans: A Y Chromosome Perspective" (PDF). Science 290 (5494): 1155–59. doi:10.1126/science.290.5494.1155. PMID 11073453. http://hpgl.stanford.edu/publications/Science_2000_v290_p1155.pdf.
- ↑ Tissue Antigens. Volume 55 Issue 1 Page 53-56, January 2000.HLA-DRB and DQB1 polymorphism in the Macedonian population.
- ↑ "GREEK HELSINKI MONITOR (GHM) &". dev.eurac.edu. http://dev.eurac.edu:8085/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1044526702223. Retrieved 2009-03-14.
- ↑ "Ethnologue report for Greece". Ethnologue. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=GR. Retrieved 2009-02-13.
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/new-multimedia/pdf/wordat077.pdf
- ↑ UCLA Language Materials Project: Language Profile.
- ↑ UCLA Language Materials Project: Language Profile.
- ↑ L. M. Danforth, The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World 1995, Princeton University Press.
- ↑ Jacques Bacid, Ph.D. Macedonia Through the Ages. Columbia University, 1983.
- ↑ Hill, P. (1999) "Macedonians in Greece and Albania: A Comparative study of recent developments". Nationalities Papers Volume 27, 1 March 1999, p. 44(14).
- ↑ Macedonia and Greece - The Struggle to Define a New Balkan Nation Macedonia and Greece - The Struggle to Define a New Balkan Nation, John Shea.
- ↑ Poulton, H.(2000), "Who are the Macedonians?",C. Hurst & Co. Publishers.
- ↑ Report about Compliance with the Principles of the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (Greece) - GREEK HELSINKI MONITOR (GHM)...those with a Macedonian national identity can be estimated to between 10,000-30,000. Indeed, the political party “Rainbow” which was created in 1994 and has campaigned for the recognition of a national Macedonian minority, received 7,300 votes in 1994 and 5,000 in 1999, two elections it contested alone: these figures correspond to some 7,000-10,000 citizens of all (not just voting) ages. One can estimate that besides this “hard core” there may be other citizens voting for mainstream parties that also espouse this identity, hence the above estimate.
- ↑ The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World, (a) pg. 221 (b) pg. 51, by Loring M. Danforth, ISBN 0-691-04356-6.
- ↑ Artan Hoxha and Alma Gurraj, Local Self-Government and Decentralization: Case of Albania. History, Reforms and Challenges. In: Local Self Government and Decentralization in South — East Europe. Proceedings of the workshop held in Zagreb, Croatia 6 April 2001. Friedrich Ebert Stiftung, Zagreb Office, Zagreb 2001, pp. 194-224 [7].
- ↑ "Landesinformationen: AlbINFO by albanien.ch". www.albanien.ch. http://www.albanien.ch/albinfo/pmwiki.php/Main/AlbGeoInfo. Retrieved 2009-03-14.
- ↑ "FOCUS Information Agency". www.focus-fen.net. http://www.focus-fen.net/?id=f1218. Retrieved 2009-03-14.
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-state=dt&-context=dt&-reg=DEC_2000_SF4_U_PCT001:001|547;&-ds_name=ACS_2004_EST_G00_&-TABLE_NAMEX=&-ci_type=A&-mt_name=ACS_2004_EST_G2000_B04003&-CONTEXT=dt&-tree_id=4001&-all_geo_types=N&-redoLog=true&-geo_id=01000US&-search_results=01000US&-format=&-_lang=en
- ↑ http://www.canadianencyclopedia.ca/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=A1SEC823709
- ↑ http://www.euroamericans.net/euroamericans.net/macedonian.htm
- ↑ http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/07/blank/key/01/01.Document.20578.xls
- ↑ Levinson & O'Leary (1992:239)
- ↑ In 1913, the majority of Macedonians in all three regions of Macedonia were Bulgarophile, i.e. they had Bulgarian identity; see: Center for Documentation and Information on Minorities in Europe, Southeast Europe (CEDIME-SE) - "Macedonians of Bulgaria", p. 14.
- ↑ The struggle for Greece, 1941-1949, Christopher Montague Woodhouse, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2002, ISBN 1850654921, p. 67.
- ↑ Who are the Macedonians? Hugh Poulton,Hurst & Co. Publishers, 1995, ISBN 1850652384, 9781850652380, p. 101.
- ↑ "The Macedonian question" published 18 January 1871.
- ↑ Балканска питања и мање историјско-политичке белешке о Балканском полуострву 1886-1905. Стојан Новаковић, Београд, 1906.
- ↑ Theodosius of Skopje Centralen D'rzhaven istoricheski archiv (Sofia) 176, op. 1. arh.ed. 595, l.5-42 - Razgledi, X/8 (1968), pp. 996-1000.
- ↑ Историја на македонската нација. Блаже Ристовски, 1999, Скопје.
- ↑ "On the Monastir Road". Herbert Corey, National Geographic, May 1917 (p. 388.)
- ↑ The Situation in Macedonia and the Tasks of IMRO (United) - published in the official newspaper of IMRO (United), "Македонско дело", N.185, April 1934.
- ↑ Резолюция о македонской нации (принятой Балканском секретариате Коминтерна — Февраль 1934 г, Москва.
- ↑ History of the Balkans, Vol. 2: Twentieth Century. Barbara Jelavich, 1983.
- ↑ Fojnica Armory, online images.
- ↑ Matkovski, Aleksandar, Grbovite na Makedonija, Skopje, 1970.
- ↑ Александар Матковски (1990) Грбовите на Македонија, Мисла, Skopje, Macedonia — ISBN 86-15-00160-X
- ↑ http://www.wipo.int/cgi-6te/guest/ifetch5?ENG+6TER+15+1151315-REVERSE+0+0+1055+F+125+431+101+25+SEP-0/HITNUM,B+KIND%2fEmblem+
- ↑ Floudas, Demetrius Andreas; ""A Name for a Conflict or a Conflict for a Name? An Analysis of Greece's Dispute with FYROM",". 24 (1996) Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 285. 1996. http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3719/is_199601/ai_n8752910. Retrieved 2007-01-24.
- ↑ http://heraldry.mol.com.mk/macedonian_symbols.htm
Further reading
- Brown, Keith, The Past in Question: Modern Macedonia and the Uncertainties of Nation, Princeton University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-691-09995-2.
- Brunnbauer, Ulf (September 2004). "Fertility, families and ethnic conflict: Macedonians and Albanians in the Republic of Macedonia, 1944-2002". Nationalities Papers 32 (3): 565–598. doi:10.1080/0090599042000246406.
- Cowan, Jane K. (ed.), Macedonia: The Politics of Identity and Difference, Pluto Press, 2000. A collection of articles.
- Danforth, Loring M., The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World, Princeton University Press, 1995. ISBN 0-691-04356-6.
- Karakasidou, Anastasia N., Fields of Wheat, Hills of Blood: Passages to Nationhood in Greek Macedonia, 1870-1990, University Of Chicago Press, 1997, ISBN 0-226-42494-4. Reviewed in Journal of Modern Greek Studies 18:2 (2000), p465.
- Mackridge, Peter, Eleni Yannakakis (eds.), Ourselves and Others: The Development of a Greek Macedonian Cultural Identity since 1912, Berg Publishers, 1997, ISBN 1-85973-138-4.
- Poulton, Hugh, Who Are the Macedonians?, Indiana University Press, 2nd ed., 2000. ISBN 0-253-21359-2.
- Roudometof, Victor, Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question, Praeger Publishers, 2002. ISBN 0-275-97648-3.
- Κωστόπουλος, Τάσος, Η απαγορευμένη γλώσσα: Η κρατική καταστολή των σλαβικών διαλέκτων στην ελληνική Μακεδονία σε όλη τη διάρκεια του 20ού αιώνα (εκδ. Μαύρη Λίστα, Αθήνα 2000). [Tasos Kostopoulos, The forbidden language: state suppression of the Slavic dialects in Greek Macedonia through the 20th century, Athens: Black List, 2000]
External links
- New Balkan Politics - Journal of Politics
- Macedonians in the UK
- United Macedonian Diaspora
- World Macedonian Congress
- House Of Immigrants
Notes
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


